The Evolution of HTTP Technology
HTTP, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is a fundamental protocol used for transferring data over the web. It has played a crucial role in shaping the way we access and interact with information online.
Originally introduced in the early 1990s, HTTP has undergone significant advancements over the years to keep pace with the ever-changing landscape of the internet. The transition from HTTP/1.1 to HTTP/2 marked a major milestone in improving web performance and efficiency.
One of the key features of HTTP/2 is its support for multiplexing, allowing multiple requests to be sent and received simultaneously over a single connection. This has led to faster loading times and enhanced user experiences across various devices.
Furthermore, the introduction of HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) has brought about a new era of security on the web. HTTPS encrypts data transmitted between a user’s browser and a website, safeguarding sensitive information from potential threats.
As we look towards the future, technologies like HTTP/3 are poised to revolutionise how data is transmitted over the internet. With its focus on performance and reliability, HTTP/3 aims to further enhance the speed and efficiency of web communications.
In conclusion, HTTP technology continues to evolve and shape the digital landscape in profound ways. From its humble beginnings to its current state of advanced protocols, HTTP remains at the core of our online experiences, driving innovation and connectivity across the globe.
Understanding HTTP: Key Questions and Insights into Web Technology
- What is HTTP and how does it work?
- What are the differences between HTTP and HTTPS?
- Why is HTTP/2 considered an improvement over HTTP/1.1?
- How does multiplexing in HTTP/2 impact web performance?
- What is the significance of HTTPS in ensuring online security?
- What advancements can we expect from technologies like HTTP/3?
What is HTTP and how does it work?
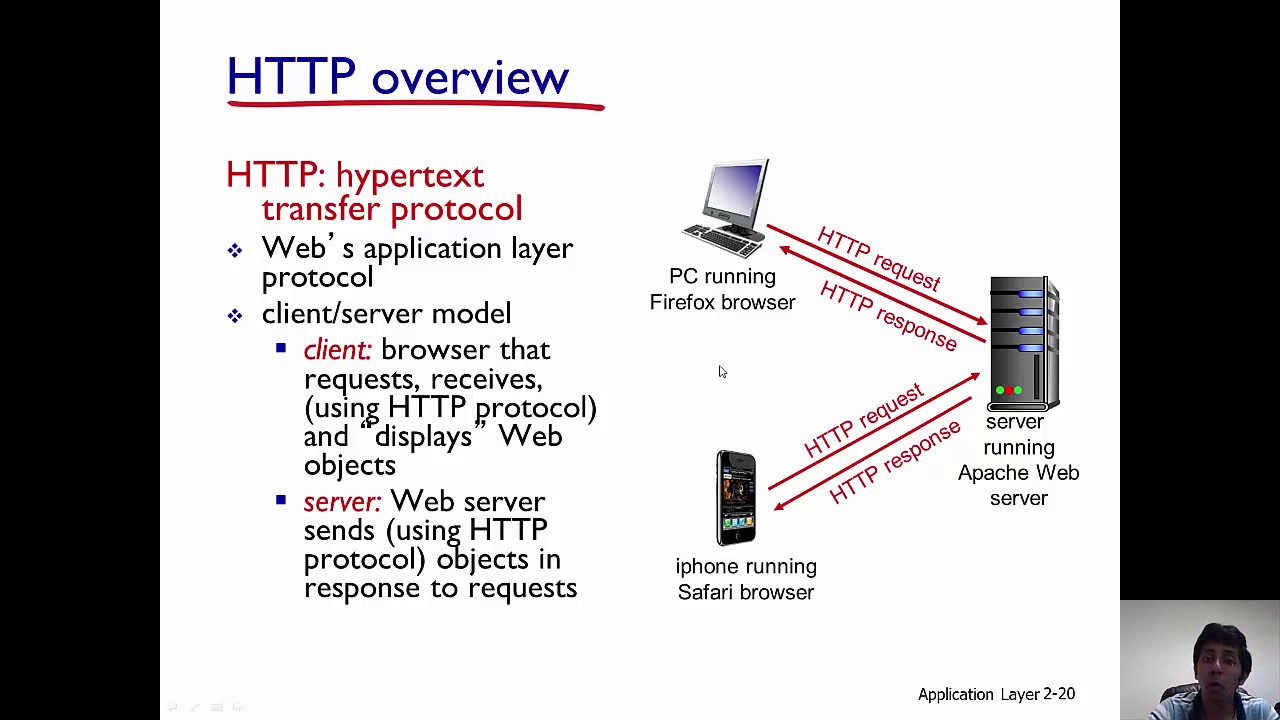
HTTP, short for Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is a fundamental protocol that facilitates the transfer of data over the internet. It serves as the foundation for communication between web servers and clients, enabling the retrieval and display of web content such as text, images, and videos. When a user requests access to a webpage by entering a URL in their browser, an HTTP request is sent to the server hosting that webpage. The server then processes the request and responds with the necessary data, which is transmitted back to the user’s browser via an HTTP response. This exchange of requests and responses forms the basis of how HTTP works, allowing seamless interaction between users and web servers across the digital realm.
What are the differences between HTTP and HTTPS?
When comparing HTTP and HTTPS, the main difference lies in their level of security. HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) transmits data over the web in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception by malicious third parties. On the other hand, HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts data during transmission, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential and protected from potential cyber threats. By incorporating encryption through SSL/TLS certificates, HTTPS provides a secure connection between the user’s browser and the website, enhancing privacy and safeguarding against data breaches. In summary, while HTTP is suitable for general browsing, HTTPS is essential for securing online transactions and protecting user privacy in today’s digital age.
Why is HTTP/2 considered an improvement over HTTP/1.1?
HTTP/2 is widely regarded as a significant improvement over HTTP/1.1 due to several key enhancements that it brings to web communication. One of the most notable features of HTTP/2 is its support for multiplexing, which allows multiple requests to be processed simultaneously over a single connection. This results in faster loading times and improved efficiency, especially for complex web pages with numerous resources. Additionally, HTTP/2 introduces header compression, reducing the overhead associated with transferring data and further enhancing performance. By addressing the limitations of its predecessor and prioritising speed and scalability, HTTP/2 has become a preferred protocol for modern web applications seeking optimal performance and user experience.
How does multiplexing in HTTP/2 impact web performance?
Multiplexing in HTTP/2 has a significant impact on web performance by allowing multiple requests and responses to be transmitted concurrently over a single connection. This means that instead of waiting for each request to be processed sequentially, multiple resources can be fetched simultaneously, leading to faster loading times and improved efficiency. By utilising multiplexing, HTTP/2 minimises latency and optimises bandwidth usage, resulting in a smoother and more responsive browsing experience for users. The ability to handle multiple streams of data efficiently enhances the overall speed and performance of websites, ultimately enhancing user satisfaction and engagement.
What is the significance of HTTPS in ensuring online security?
The significance of HTTPS in ensuring online security cannot be overstated. HTTPS, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data transmitted between a user’s browser and a website. By encrypting this data, HTTPS prevents malicious actors from intercepting and tampering with the information exchanged over the internet. This encryption not only protects users’ personal details, such as login credentials and payment information, but also helps establish trust between users and websites. In an age where cyber threats are prevalent, adopting HTTPS is essential for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of online communications, thereby enhancing overall security measures on the web.
What advancements can we expect from technologies like HTTP/3?
Technologies like HTTP/3 are expected to bring significant advancements in the realm of web communications. With a focus on enhancing performance and reliability, HTTP/3 introduces improvements such as a more efficient data transfer protocol, reduced latency, and enhanced security measures. By leveraging features like QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections) and prioritised streaming, HTTP/3 aims to streamline the process of transmitting data over the internet, resulting in faster loading times and improved overall user experiences. Additionally, the adoption of HTTP/3 is anticipated to revolutionise how websites and applications communicate with servers, paving the way for a more seamless and responsive online environment.