The Evolution of HTTP Technology
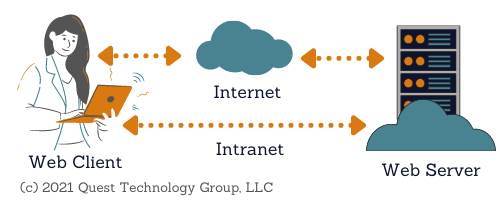
HTTP, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is a fundamental protocol that underpins the World Wide Web. It serves as the foundation for communication between web servers and clients, enabling the transfer of data and information across the internet.
Since its inception in the early 1990s, HTTP has undergone significant evolution to keep pace with the changing landscape of the internet. The most widely used version, HTTP/1.1, has been instrumental in shaping the way we access and interact with online content.
Key Features of HTTP/1.1:
- Persistent Connections: Unlike its predecessor, HTTP/1.0, which required establishing a new connection for each request/response cycle, HTTP/1.1 introduced persistent connections to reduce latency and improve efficiency.
- Pipelining: Pipelining allows multiple requests to be sent over a single connection without waiting for each response, further enhancing performance by reducing overhead.
- Caching: Caching mechanisms in HTTP/1.1 enable browsers to store and reuse previously fetched resources, reducing load times and network traffic.
The Rise of HTTP/2:
In 2015, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) introduced HTTP/2 as a successor to HTTP/1.1 with a focus on improving speed and efficiency. Key features of HTTP/2 include multiplexing, header compression, prioritisation of requests, and server push capabilities.
By allowing multiple concurrent requests/responses over a single connection through multiplexing and reducing overhead with header compression, HTTP/2 significantly enhances performance compared to its predecessor.
The Future: HTTP/3 and Beyond
With the emergence of new technologies and demands for even faster web experiences, protocols like QUIC have paved the way for the development of HTTP/3. Building on QUIC’s principles of reduced latency and improved security through encryption by default, HTTP/3 aims to further enhance web performance in an evolving digital landscape.
As we look towards an increasingly interconnected future driven by IoT devices, AI-powered applications, and immersive experiences, the evolution of HTTP technology will continue to play a crucial role in shaping how we access and interact with online content.
9 Essential Tips for Mastering HTTP Technology and Enhancing Web Security
- Use HTTPS to ensure secure communication over the internet.
- Understand the difference between HTTP and HTTPS protocols.
- Implement proper redirection from HTTP to HTTPS for improved security.
- Optimize website performance by reducing unnecessary HTTP requests.
- Leverage caching mechanisms to speed up content delivery over HTTP.
- Be mindful of potential security vulnerabilities in HTTP-based applications.
- Regularly update server configurations to adhere to best practices in HTTP technology.
- Consider using Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) for faster loading times via HTTP.
- Monitor and analyse network traffic for any anomalies or suspicious activities related to HTTP.
Use HTTPS to ensure secure communication over the internet.
Using HTTPS is essential to guarantee secure communication over the internet. By encrypting data exchanged between a user’s browser and a website’s server, HTTPS helps protect sensitive information such as login credentials, payment details, and personal data from potential cyber threats. This added layer of security not only ensures the confidentiality and integrity of transmitted data but also builds trust with users by demonstrating a commitment to safeguarding their online interactions. Embracing HTTPS is a proactive step towards enhancing cybersecurity and promoting a safe browsing experience for all internet users.
Understand the difference between HTTP and HTTPS protocols.
It is crucial to understand the distinction between HTTP and HTTPS protocols when navigating the web. While HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) transfers data in plain text, leaving it vulnerable to interception, HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts data during transmission, ensuring a secure and private connection between the user’s browser and the website. By opting for websites with HTTPS protocol, users can protect their sensitive information and enhance their online security.
Implement proper redirection from HTTP to HTTPS for improved security.
Implementing proper redirection from HTTP to HTTPS is crucial for enhancing security on websites. By ensuring that all communication is encrypted and secure, users can trust that their data remains protected from potential threats and vulnerabilities. HTTPS not only safeguards sensitive information but also builds credibility and trust with visitors. Making this simple yet effective transition to HTTPS demonstrates a commitment to security best practices and helps create a safer online environment for both website owners and users alike.
Optimize website performance by reducing unnecessary HTTP requests.
To enhance website performance, it is essential to optimise by minimising unnecessary HTTP requests. Each HTTP request adds to the loading time of a webpage, so reducing the number of requests can significantly improve site speed. By combining files, using CSS sprites, and implementing techniques like lazy loading for images, web developers can streamline the loading process and create a more efficient user experience. Prioritising which resources are essential for initial page rendering and deferring non-critical requests can help in achieving faster load times and better overall performance for websites.
Leverage caching mechanisms to speed up content delivery over HTTP.
By utilising caching mechanisms, you can enhance the speed of content delivery over HTTP. Caching allows browsers to store previously fetched resources, reducing the need to re-fetch them from the server. This not only accelerates the loading time of web pages but also minimises network traffic, resulting in a more efficient and seamless user experience. By leveraging caching effectively, websites can optimise performance and provide users with quicker access to content, ultimately improving overall satisfaction and engagement.
Be mindful of potential security vulnerabilities in HTTP-based applications.
When utilising HTTP-based applications, it is essential to be vigilant about potential security vulnerabilities that may arise. As HTTP transmits data in plain text, sensitive information such as login credentials or personal details can be intercepted by malicious actors. To mitigate these risks, consider implementing additional security measures such as using HTTPS encryption protocols to safeguard data transmission and protect user privacy. Regularly updating software and monitoring for security threats are also crucial steps in ensuring the safety and integrity of HTTP-based applications.
Regularly update server configurations to adhere to best practices in HTTP technology.
It is essential to regularly update server configurations to align with the best practices in HTTP technology. By staying up-to-date with the latest standards and guidelines, such as implementing secure encryption protocols, optimising caching mechanisms, and prioritising content delivery, organisations can ensure optimal performance, enhanced security, and improved user experiences on their websites. Keeping server configurations in line with current HTTP technology recommendations not only boosts efficiency but also helps mitigate potential vulnerabilities and ensures seamless communication between servers and clients across the web.
Consider using Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) for faster loading times via HTTP.
Consider utilising Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to enhance loading times through HTTP. CDNs distribute website content across multiple servers geographically closer to users, reducing latency and improving overall performance. By leveraging CDNs, you can deliver web assets more efficiently, ensuring faster loading times and a smoother browsing experience for your visitors.
Monitor and analyse network traffic for any anomalies or suspicious activities related to HTTP.
It is crucial to monitor and analyse network traffic for any anomalies or suspicious activities related to HTTP. By keeping a close eye on the data being transmitted over the network, organisations can detect potential security threats such as malicious attacks, data breaches, or unauthorised access attempts. Monitoring HTTP traffic allows for the early identification of irregular patterns or unusual behaviours that may indicate a security breach, enabling prompt action to mitigate risks and safeguard sensitive information. Regular analysis of network traffic helps maintain a secure online environment and ensures the integrity of data exchanges over HTTP protocols.